# Waves Node
A node is a crucial component of the blockchain network. It stores a copy of the blockchain data and synchronizes the data with other nodes. The decentralized network is maintained by hundreds of independent nodes, ensuring that no single entity has sole control over the network or the ability to manipulate data.
Waves is a public blockchain that allows anyone to launch their own node and join the network. The Waves application can be installed and run on an ordinary computer. Installation options are given in the Install Waves Node article.
Any node can propose new transactions that will propagate in the network until they are included in a block or discarded. Having WAVES on the node's balance is only required for block generation.
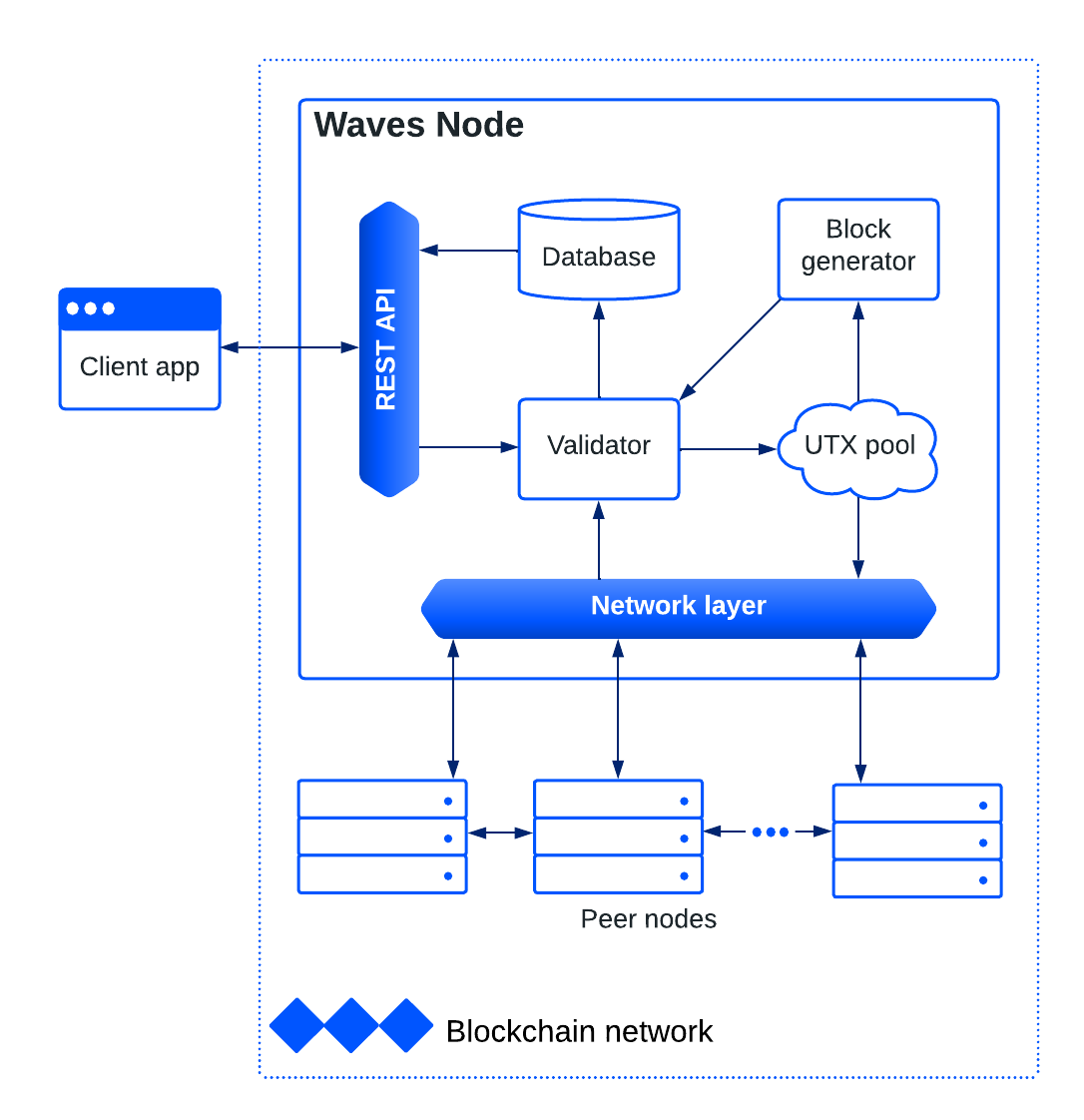
# Node Architecture
The main components of the Waves node are as follows:
- Network layer provides interaction with peer nodes.
- Validator checks transactions and blocks against blockchain rules.
- Database stores validated and confirmed transactions and blocks, as well as the current state of the blockchain: balances of accounts, entries of account data storages, assigned scripts etc.
- UTX pool contains unconfirmed transactions until they are included in a block.
- Block generator creates blocks that are added to the blockchain.
- Node REST API is an interface for receiving blockchain data, sending transactions to the blockchain, and more. For detailed information, see the Node REST API.
# Validating Node
A validating node checks transactions and blocks received from other nodes against blockchain rules. Validation implicates ensuring that the block format is correct, all hashes in the block are computed correctly, the block contains the hash of the previous one, as well as calculating transaction execution results, including scripts involved (see Transaction Validation for details). Non-valid transactions and blocks are discarded.
Any Waves node works as a validating node by default, unless otherwise specified in its settings.
# Light Node
A light node does not validate transactions received from other nodes. Instead of executing transactions, the node applies ready-made snapshots to the blockchain state. More about snapshots
Running a node in the light mode can significantly speed up block processing under heavy load. However, a light node stores all the blockchain data and can be switched to validation mode without downloading additional data.
Light mode is enabled by feature #22 “Light Node”.
# Generating Node
A node with a generating balance of at least 1000 WAVES can participate in block generation and receive rewards. Generating node can be either a validating or a light node. The node's chance to generate a block is proportional to its generating balance, according to the Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS) algorithm.
The generating balance of an account is its lowest balance in WAVES considering leasing over the last 1000 blocks. The leasing mechanic allows nodes to attract funds from users to increase their generating balance, frequency of block generation, and resulting income. More about leasing
Keep in mind that a node with a minimum balance of 1000 WAVES generates only about one block per month. Without a significant amount of WAVES, it is better to participate in block generation by leasing WAVES to higher-performance generators.
The list of generating nodes in the Waves network, their balances, and block statistics are available at w8.io.
To run a generating node and receive rewards, follow the instructions.
# Generator's Income
Block generators receive rewards for adding a new block to the blockchain:
- Generator's share of the block reward. The current block reward is 6 WAVES, of which the generator receives 2 WAVES. Once feature #23 "Boost Block Reward" is activated, the block reward will be 60 WAVES, the generator's share will be 20 WAVES (the multiplier of ×10 applies within 300,000 blocks on Mainnet).
- Waves DAO LP tokens (WAVESDLP) corresponding to Waves DAO's share of the block reward.
- Transaction fees. The node receives 40% of the total fees for transactions in the current block and 60% of the total fees for transactions in the previous block, according to Waves-NG protocol.
The calculation of the rewards is described in more detail in the Generator's Income article.
# Apps
To develop and run a decentralized application, you do not have to run your own node. You can receive blockchain data and send transactions signed by users via API of pool of public nodes.
However, running your own node provides you with additional options:
- interact with the node without network latency,
- make more frequent requests than allowed by the limitations of the public pool,
- customize the node configuration with respect to your app,
- install node extensions, for example, Blockchain Updates to track changes,
- create your own node extensions.
# Node Scala and Node Go
The Waves node has two implementations:
- Node Scala is the main version providing maximum functionality.
- Node Go is the alternative version focused on high operation speed and interaction with gPRC services. Node Go is currently under development and not recommended to use in mission-critical projects.
Running two different applications in parallel makes the Waves network more sustainable to protocol implementation errors. Differences between the two versions are highlighted in the Node Go article.