# Waves Basics
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that ensures data immutability and transparency.
# Transactions and Blocks
Blockchain data is presented as transactions. A transaction is a record of an action, such as token issue, token transfer, smart contract creation or invocation, etc.
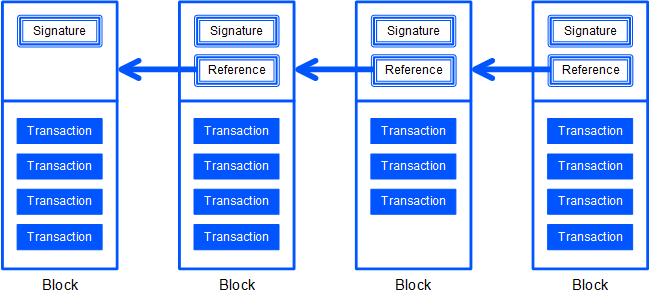
Transactions are stacked into blocks. Besides transactions, every block contains the hash of the previous block and the digital signature of the node that generated the block. The previous block contains the data hash of its preceding block, and so on. As a result, the signature of each block depends on the data of all the preceding blocks.
In other words, the blockchain is a sequence of blocks linked by cryptographic hashes. Each transaction stays intact indefinitely. An attempt to change any data in a block would invalidate the block and all the later blocks.
# Node
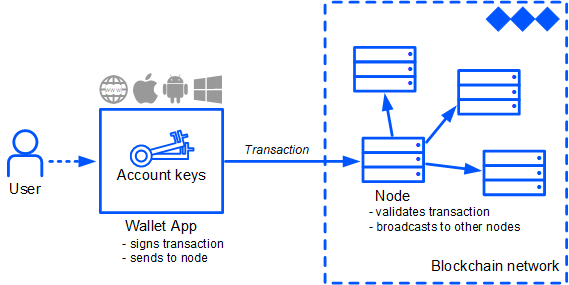
A node is a computer that serves the blockchain network. The Waves node stores a full copy of the blockchain data, validates transactions and blocks, verifies signatures and hashes, and synchronizes the data with other nodes.
The Waves network consists of hundreds of nodes hosted around the world. This ensures that the blockchain data is protected against counterfeit or deletion, malicious or occasional. Everyone can launch a node and join the network.
The node that holds at least 1,000 WAVES (by ownership or lease), can participate in block generation and receive transaction fees and their share of block reward. The more tokens the node holds, the greater is its chance to add the next block.
# Account
Waves uses an account-based model. Each transaction is created on behalf of an account, all assets and data are associated with the account. An account has a pair of cryptographically bound keys: a private key that the account uses to sign transactions, and a public key that allows anyone to verify the signature. More about account
To create an account, store keys, and sign transactions, you can use applications developed by Waves community: Keeper Wallet, WX Network, WavesFX, or others.
# dApp
A decentralized application (dApp) is an application empowered by blockchain. A dApp can store data on the blockchain and invoke a script assigned to an account. There is, therefore, no centralized database that might be hacked or compromised. Any user can view the script code and the result of its invocation.
Learn more about Waves technology and gain the hands-on skills needed to build dApps using Waves lessons.