# What is dApp
dApp is Waves account assigned with dApp script.
dApp script is a Ride script that contains callable functions that can be called externally by the invoke script transaction.
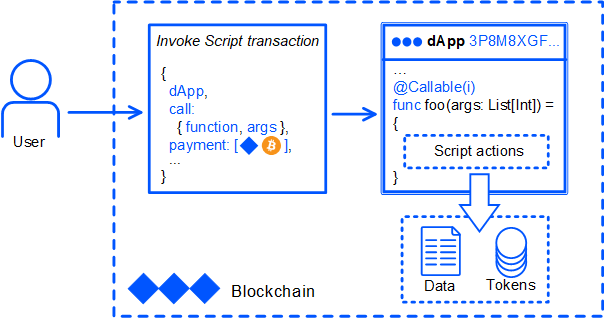
An invoke script transaction contains:
- dApp address;
- name of the callable function and the argument values;
- in addition, an invoke script transaction can contain payments to be credited to the dApp balance.
Invoke script transaction example
You can use callable functions to:
- Add, modify or delete dApp account data storage entries.
- Transfer, issue, reissue, burn tokens.
- Setup sponsorship.
Available script actions depend on Standard library version used.
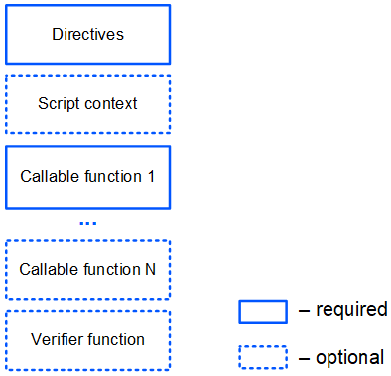
# Structure of dApp Script
dApp script comprises one or more callable functions.
In addition, dApp script can comprise a verifier function that checks transactions and orders that are sent from dApp account.
# Directives
Each Ride script should start with directives. Here is the set of directives for the dApp script:
{-# STDLIB_VERSION 8 #-}
{-# CONTENT_TYPE DAPP #-}
{-# SCRIPT_TYPE ACCOUNT #-}
These directives tell the compiler that:
- The script uses Standard library version 8.
- Type of the script is dApp.
- The script will be assigned to an account (not asset).
# Script Context
Script context includes built-in variables and built-in functions. In addition, user variables and functions could be declared between directives and callable function. These variables and functions are accessible within the entire script.
Example:
let someConstant = 42
func doSomething() = {
1+1
}
# Callable Functions
Callable function can be called externally by the invoke script transaction. The callable function should be marked with the @Callable(i) annotation, where i is an Invocation structure that contains invoke script transaction fields that are available to the callable function.
Callable function result is a set of script actions that are performed on the blockchain: adding entries to the account data storages, token transfers and others. The result format and the possible actions depend on the Standard library version used.
For a detailed description, see the Callable Function article.
In the example below the callable function transfers 1 WAVES to an account that called it and records the request information in the account data storage. If the same account tries to call the function again, the callable function does nothing.
@Callable(i)
func faucet () = {
let isKnownCaller = match getBoolean(this, toBase58String(i.caller.bytes)) {
case hist: Boolean =>
hist
case _ =>
false
}
if (!isKnownCaller) then
(
[
BooleanEntry(toBase58String(i.caller.bytes), true),
ScriptTransfer(i.caller, 100000000, unit)
],
unit
)
else ([],unit)
}
# Verifier Function
Verifier function checks transactions and orders that are sent from dApp account (in other words it does the same as the account script). The verifier function should be marked with the @Verifier(tx) annotation, where tx is the transaction or the order that that the function is currently checking.
For a detailed description, see the Verifier Function article.
In the example below the verifier function allows transfer transactions and denies orders and other types of transactions. The match operator is used to specify verification rules depending on the type of transaction (or order).
@Verifier(tx)
func verify() = {
match tx {
case ttx:TransferTransaction => sigVerify(ttx.bodyBytes, ttx.proofs[0], ttx.senderPublicKey)
case _ => false
}
}
dApp that has no verifier function performs default verification, that is, checking that the transaction or the order is indeed signed by this account.
# Data Accessible by dApp
dApps can read the following blockchain data:
- Entries in account data storages (both dApp's account and any other account).
- Balances of accounts.
- Parameters of assets.
- Blockchain height.
- Headers of blocks.
- Transfer transactions (by transaction ID).
Appropriate fuctions are described in the Account Data Storage Functions and Blockchain Functions articles.
Furthermore:
- The callable function has access to some fields of the transaction that called the dApp script. See the Invocation article for the fields description.
- The verifier function has access to the fields of the outgoing transaction or order, including proofs.
# Assigning dApp Script to Account
To assign dApp script to an account, you have to send a Set Script transaction from this account.
There are the following options to send the transaction:
- In Waves IDE create or import an account, open the dApp script and click Deploy.
- Using client libraries. See some examples of sending a transaction in the Creating & Broadcasting Transactions article.
Set script transaction example
The fee for the Set Script transaction is 0.01 WAVES.
If the script contains a verifier function and the complexity of the function exceeds the sender complexity threshold, the minimum fee for each transaction sent from the dApp account is increased by 0.004 WAVES.
# Limitations
Limitations on the size, complexity of the script, as well as on functions and variables are given in the Limitations article.
# Examples
Find dApp script examples:
- In the How-to Guides chapter.
- In Waves IDE in the Library menu.
- In Github repository ride-examples.
For tutorial on creating dApp, see the Creating & Launching dApp article.
# Waves Tech Blog Articles
- Why use the Waves protocol for DeFi applications? (Mar 25, 2021)
- 5 things I wish I’d known before starting to develop dApps (Jun 17, 2020)
- How to build a dApp for team motivation (Jun 9, 2020)
- How to avoid common mistakes in dApp development (May 8, 2020)
- What are Smart Contracts and how to use them in your app (Mar 19, 2020)